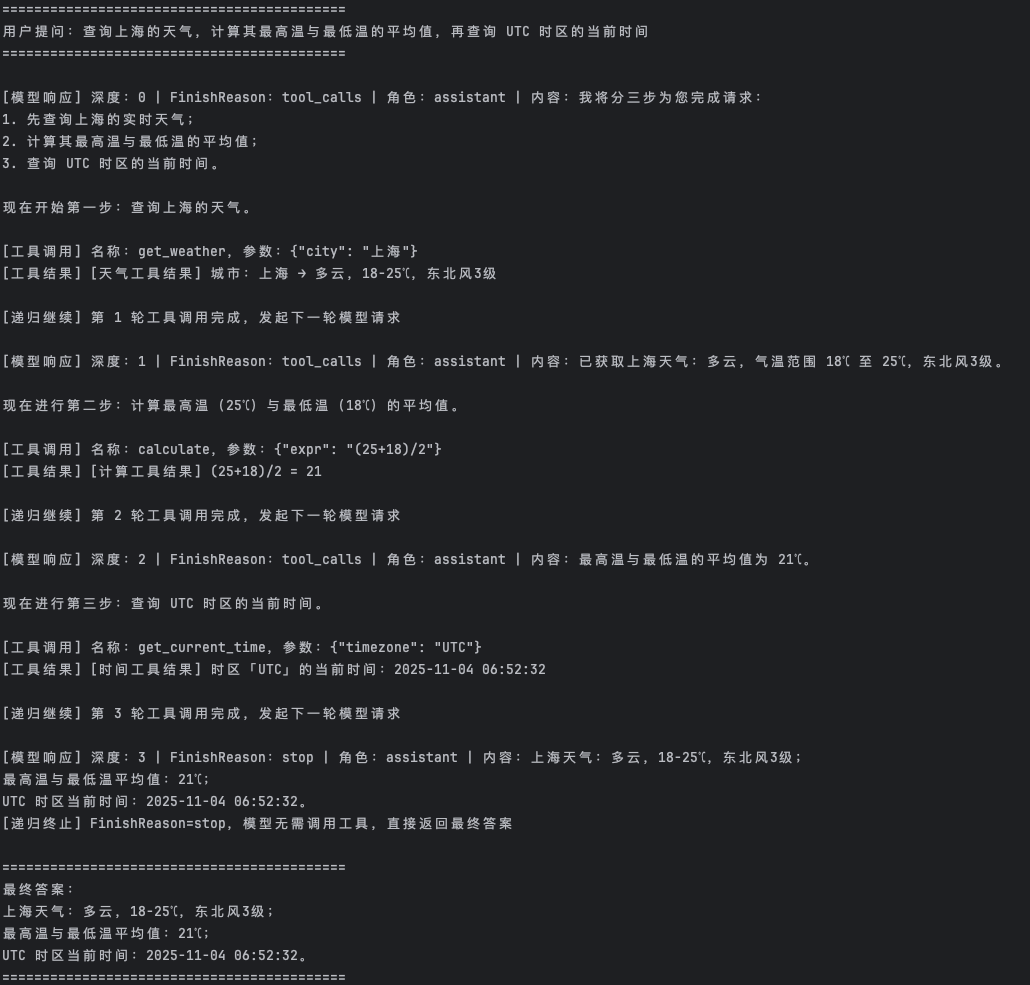
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
301
302
303
304
305
306
307
308
309
310
311
312
313
314
315
316
317
318
319
320
321
322
323
324
325
326
327
328
329
330
331
332
333
334
335
336
337
338
339
340
341
342
343
344
345
346
347
348
349
350
351
352
353
354
355
356
357
358
359
360
361
362
363
364
365
366
367
368
369
370
371
372
373
| package main
import (
"context"
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"math"
"time"
"github.com/sashabaranov/go-openai"
"github.com/sashabaranov/go-openai/jsonschema"
)
// ========================== 1. 工具参数结构体(用于解析工具调用结果) ==========================
// 天气查询参数(仅用于解析模型返回的工具调用参数,无需额外标签)
type WeatherParams struct {
City string `json:"city"`
}
// 数学计算参数
type CalcParams struct {
Expr string `json:"expr"`
}
// 时间查询参数
type TimeParams struct {
Timezone string `json:"timezone"`
}
// ========================== 2. 工具实现逻辑(无修改) ==========================
// 天气查询工具(模拟第三方 API 调用)
func getWeather(ctx context.Context, city string) (string, error) {
// 超时控制(3秒)
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(ctx, 3*time.Second)
defer cancel()
// 模拟 API 网络延迟
select {
case <-ctx.Done():
return "", fmt.Errorf("查询超时:%v", ctx.Err())
case <-time.After(500 * time.Millisecond):
}
// 模拟天气数据
weatherMap := map[string]string{
"北京": "晴,20-28℃,微风",
"上海": "多云,18-25℃,东北风3级",
"广州": "雷阵雨,22-26℃,南风2级",
"深圳": "阴,23-27℃,东风2级",
"杭州": "晴转多云,19-26℃,西北风2级",
}
if weather, ok := weatherMap[city]; ok {
return fmt.Sprintf("[天气工具结果] 城市:%s → %s", city, weather), nil
}
return fmt.Sprintf("[天气工具结果] 未查询到「%s」的天气数据(支持城市:北京、上海、广州、深圳、杭州)", city), nil
}
// 数学计算工具(支持基础运算)
func calculate(ctx context.Context, expr string) (string, error) {
// 超时控制(2秒)
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(ctx, 2*time.Second)
defer cancel()
// 模拟计算延迟
select {
case <-ctx.Done():
return "", fmt.Errorf("计算超时:%v", ctx.Err())
case <-time.After(300 * time.Millisecond):
}
// 支持的表达式逻辑
switch expr {
case "100*200":
return fmt.Sprintf("[计算工具结果] %s = %d", expr, 100*200), nil
case "sqrt(16)":
return fmt.Sprintf("[计算工具结果] %s = %.2f", expr, math.Sqrt(16)), nil
case "(25+18)/2":
return fmt.Sprintf("[计算工具结果] %s = %d", expr, (25+18)/2), nil
case "200/5":
return fmt.Sprintf("[计算工具结果] %s = %d", expr, 200/5), nil
case "(18+25)/2":
return fmt.Sprintf("[计算工具结果] %s = %.1f", expr, (18+25)/2.0), nil
default:
return fmt.Sprintf("[计算工具结果] 暂不支持表达式:%s(当前支持:100*200、sqrt(16)、(a+b)/2、a/b)", expr), nil
}
}
// 时间查询工具(支持多时区)
func getCurrentTime(ctx context.Context, timezone string) (string, error) {
// 超时控制(1秒)
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(ctx, 1*time.Second)
defer cancel()
// 模拟查询延迟
select {
case <-ctx.Done():
return "", fmt.Errorf("时间查询超时:%v", ctx.Err())
case <-time.After(200 * time.Millisecond):
}
// 默认时区处理(未传时区时用上海时区)
if timezone == "" {
timezone = "Asia/Shanghai"
}
// 加载时区并格式化时间
loc, err := time.LoadLocation(timezone)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Sprintf("[时间工具结果] 无效时区:%s(示例有效时区:Asia/Shanghai、UTC、America/New_York)", timezone), nil
}
currentTime := time.Now().In(loc).Format("2006-01-02 15:04:05")
return fmt.Sprintf("[时间工具结果] 时区「%s」的当前时间:%s", timezone, currentTime), nil
}
// ========================== 3. 核心修改:用 go-openai/jsonschema 定义工具参数 ==========================
// getOpenAITools:通过 jsonschema.Definition 构建 OpenAI 工具定义
func getOpenAITools() []openai.Tool {
// -------------------------- 3.1 天气工具参数(jsonschema 定义) --------------------------
weatherCityParam := jsonschema.Definition{
Type: jsonschema.String, // 参数类型:字符串
Description: "城市名称(如北京、上海,仅支持国内主流城市)", // 参数描述
}
// 天气工具的整体参数 Schema(对象类型,包含 city 字段)
weatherParamsSchema := jsonschema.Definition{
Type: jsonschema.Object,
Properties: map[string]jsonschema.Definition{"city": weatherCityParam},
Required: []string{"city"}, // 明确必传字段列表
}
// -------------------------- 3.2 计算工具参数(jsonschema 定义) --------------------------
calcExprParam := jsonschema.Definition{
Type: jsonschema.String,
Description: "数学表达式(支持乘法*、除法/、开方sqrt()、两数平均值(a+b)/2)",
}
calcParamsSchema := jsonschema.Definition{
Type: jsonschema.Object,
Properties: map[string]jsonschema.Definition{"expr": calcExprParam},
Required: []string{"expr"},
}
// -------------------------- 3.3 时间工具参数(jsonschema 定义) --------------------------
timezoneParam := jsonschema.Definition{
Type: jsonschema.String,
Description: "时区(如 Asia/Shanghai 表示上海时区,UTC 表示世界协调时间)",
}
timeParamsSchema := jsonschema.Definition{
Type: jsonschema.Object,
Properties: map[string]jsonschema.Definition{"timezone": timezoneParam},
Required: []string{}, // 无必传字段
}
// -------------------------- 3.4 组装 OpenAI 工具列表 --------------------------
return []openai.Tool{
{
Type: openai.ToolTypeFunction,
Function: &openai.FunctionDefinition{
Name: "get_weather", // 工具名称(模型调用时使用)
Description: "查询指定城市的实时天气(包含气温、天气状况、风力信息)", // 工具描述(帮助模型判断是否需要调用)
Parameters: weatherParamsSchema, // 绑定上述定义的参数 Schema
},
},
{
Type: openai.ToolTypeFunction,
Function: &openai.FunctionDefinition{
Name: "calculate",
Description: "执行基础数学计算(支持四则运算和简单函数,不支持复杂公式)",
Parameters: calcParamsSchema,
},
},
{
Type: openai.ToolTypeFunction,
Function: &openai.FunctionDefinition{
Name: "get_current_time",
Description: "查询指定时区的当前时间(默认返回上海时区时间,支持全球主流时区)",
Parameters: timeParamsSchema,
},
},
}
}
// ========================== 4. 工具调用执行器(解析+执行) ==========================
func executeToolCall(ctx context.Context, toolCall openai.ToolCall) (string, error) {
fmt.Printf("\n[工具调用] 名称:%s,参数:%s\n", toolCall.Function.Name, toolCall.Function.Arguments)
// 根据工具名称分发执行
switch toolCall.Function.Name {
case "get_weather":
// 解析工具参数(绑定到 WeatherParams 结构体)
var params WeatherParams
if err := json.Unmarshal([]byte(toolCall.Function.Arguments), ¶ms); err != nil {
return "", fmt.Errorf("参数解析失败:%v(请检查是否传入 city 字段)", err)
}
// 参数校验(兜底,防止模型未传必传参数)
if params.City == "" {
return "", fmt.Errorf("城市名称不能为空(工具要求必传 city 参数)")
}
return getWeather(ctx, params.City)
case "calculate":
var params CalcParams
if err := json.Unmarshal([]byte(toolCall.Function.Arguments), ¶ms); err != nil {
return "", fmt.Errorf("参数解析失败:%v(请检查是否传入 expr 字段)", err)
}
if params.Expr == "" {
return "", fmt.Errorf("数学表达式不能为空(工具要求必传 expr 参数)")
}
return calculate(ctx, params.Expr)
case "get_current_time":
var params TimeParams
if err := json.Unmarshal([]byte(toolCall.Function.Arguments), ¶ms); err != nil {
return "", fmt.Errorf("参数解析失败:%v(请检查 timezone 字段格式)", err)
}
// 未传时区时使用默认值(工具定义中已声明,此处兜底)
if params.Timezone == "" {
params.Timezone = "Asia/Shanghai"
}
return getCurrentTime(ctx, params.Timezone)
default:
return "", fmt.Errorf("未知工具:%s(当前支持工具:get_weather、calculate、get_current_time)", toolCall.Function.Name)
}
}
// ========================== 5. 递归多轮工具调用逻辑(FinishReason 校验) ==========================
const maxRecursionDepth = 5 // 最大递归深度(防止无限循环)
func recursiveAgent(ctx context.Context, client *openai.Client, messages []openai.ChatCompletionMessage, depth int) (string, error) {
// 1. 递归深度限制:超过阈值直接终止(避免模型逻辑异常导致循环)
if depth > maxRecursionDepth {
errMsg := fmt.Sprintf("递归深度超过阈值(最大 %d 轮),可能存在工具调用循环或模型逻辑异常", maxRecursionDepth)
fmt.Println("[错误]", errMsg)
return "", fmt.Errorf(errMsg)
}
// 2. 调用 OpenAI 模型(传入工具定义,让模型判断是否调用工具)
resp, err := client.CreateChatCompletion(ctx, openai.ChatCompletionRequest{
Model: "Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B-Instruct", // 必须使用支持函数调用的模型(gpt-4o 更优)
Messages: messages, // 上下文消息(包含历史交互记录)
Tools: getOpenAITools(), // 传入用 jsonschema 定义的工具列表
ToolChoice: openai.ChunkingStrategyTypeAuto, // 模型自主判断是否调用工具
Temperature: 0.3, // 降低随机性,确保工具调用逻辑稳定
MaxTokens: 1024, // 限制单轮响应长度,避免 token 不足
})
if err != nil {
return "", fmt.Errorf("模型请求失败:%v(请检查 API Key 和网络连接)", err)
}
// 提取模型响应核心信息
choice := resp.Choices[0]
modelMsg := choice.Message
finishReason := choice.FinishReason
// 打印调试日志(便于跟踪调用流程)
fmt.Printf("\n[模型响应] 深度:%d | FinishReason:%s | 角色:%s | 内容:%s\n",
depth, finishReason, modelMsg.Role, modelMsg.Content)
// 3. 将模型响应加入上下文(关键:保存所有交互历史,让模型追溯前序步骤)
messages = append(messages, modelMsg)
// 4. 根据 FinishReason 分支处理(核心逻辑:判断是否继续调用工具)
switch finishReason {
case openai.FinishReasonStop:
// 场景1:模型正常终止(无需工具)→ 返回最终答案
fmt.Println("[递归终止] FinishReason=stop,模型无需调用工具,直接返回最终答案")
return modelMsg.Content, nil
case openai.FinishReasonToolCalls:
// 场景2:模型明确需要调用工具 → 执行工具并递归
if len(modelMsg.ToolCalls) == 0 {
errMsg := "异常:FinishReason=function_call,但模型未返回任何工具调用指令(可能是模型响应不完整)"
fmt.Println("[错误]", errMsg)
return "", fmt.Errorf(errMsg)
}
// 执行所有工具调用(支持单次多工具并行调用)
for _, toolCall := range modelMsg.ToolCalls {
toolResult, err := executeToolCall(ctx, toolCall)
if err != nil {
// 工具执行失败:将错误信息加入上下文,让模型决定是否重试或告知用户
errorMsg := fmt.Sprintf("[工具调用失败] 工具:%s | 错误:%v", toolCall.Function.Name, err)
fmt.Println(errorMsg)
messages = append(messages, openai.ChatCompletionMessage{
Role: openai.ChatMessageRoleTool,
Name: toolCall.Function.Name,
Content: errorMsg,
ToolCallID: toolCall.ID, // 必须关联工具调用 ID,模型才能对应上下文
})
continue
}
// 工具执行成功:将结果加入上下文,供模型后续整理答案
fmt.Printf("[工具结果] %s\n", toolResult)
messages = append(messages, openai.ChatCompletionMessage{
Role: openai.ChatMessageRoleTool,
Name: toolCall.Function.Name,
Content: toolResult,
ToolCallID: toolCall.ID,
})
}
// 递归继续:传入更新后的上下文,发起下一轮模型请求(深度+1)
fmt.Printf("\n[递归继续] 第 %d 轮工具调用完成,发起下一轮模型请求\n", depth+1)
return recursiveAgent(ctx, client, messages, depth+1)
case openai.FinishReasonLength:
// 场景3:token 不足导致响应截断 → 提示用户增大 MaxTokens
errMsg := "模型响应因 token 长度限制被截断 → 解决方案:将 MaxTokens 参数从 1024 增大(如 2048)"
fmt.Println("[错误]", errMsg)
return "", fmt.Errorf(errMsg)
case openai.FinishReasonContentFilter:
// 场景4:内容被过滤 → 告知用户无法处理
errMsg := "模型响应因内容过滤政策被截断(可能包含敏感信息),无法继续处理"
fmt.Println("[错误]", errMsg)
return "", fmt.Errorf(errMsg)
case openai.FinishReasonNull:
// 场景5:响应不完整(如流式响应未结束)→ 提示网络异常
errMsg := "模型响应不完整,可能是网络波动或 API 服务临时故障"
fmt.Println("[错误]", errMsg)
return "", fmt.Errorf(errMsg)
default:
// 场景6:未知 FinishReason → 降级终止
errMsg := fmt.Sprintf("未知的 FinishReason:%s,为避免异常终止递归调用", finishReason)
fmt.Println("[错误]", errMsg)
return "", fmt.Errorf(errMsg)
}
}
// ========================== 6. 完整的 main 方法 ==========================
func main() {
// 1. 校验 OpenAI API Key(必须设置环境变量)
//apiKey := os.Getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY")
config := openai.DefaultConfig("xxx")
config.BaseURL = "xxx"
client := openai.NewClientWithConfig(config)
ctx := context.Background()
userQuery := "查询上海的天气,计算其最高温与最低温的平均值,再查询 UTC 时区的当前时间"
fmt.Printf("===========================================\n")
fmt.Printf("用户提问:%s\n", userQuery)
fmt.Printf("===========================================\n")
initMessages := []openai.ChatCompletionMessage{
{
Role: openai.ChatMessageRoleSystem,
Content: `你是一个智能 AI Agent,严格按照以下规则工作:
1. 必须根据用户问题,自主判断是否需要调用工具(天气、计算、时间);
2. 若需要多步工具调用,需逐步执行,直到获取所有必要信息后再整理答案;
3. 工具返回结果后,用自然语言清晰、简洁地回复用户,无需额外冗余信息;
4. 若工具调用失败,需告知用户失败原因,无需继续重试。`,
},
{
Role: openai.ChatMessageRoleUser,
Content: userQuery,
},
}
finalAnswer, err := recursiveAgent(ctx, client, initMessages, 0)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("\n===========================================\n")
fmt.Printf("执行失败:%v\n", err)
fmt.Printf("===========================================\n")
return
}
fmt.Printf("\n===========================================\n")
fmt.Printf("最终答案:\n%s\n", finalAnswer)
fmt.Printf("===========================================\n")
}
|